In the contemporary digital landscape, the preservation of online privacy and the fortification of cybersecurity protocols have ascended to a position of critical importance.
A foundational and exceptionally potent mechanism for realizing these objectives is the implementation of a Virtual Private Network (VPN).
Among the various solutions available, OpenVPN distinguishes itself as an advanced, open-source VPN protocol and application renowned for its formidable security architecture and inherent operational flexibility.
The following treatise provides a comprehensive, systematic methodology for the deployment of the OpenVPN solution upon a Virtual Private Server (VPS).
This detailed exposition is specifically tailored to benefit a broad spectrum of users, including dedicated Information Technology (IT) professionals, experienced system administrators, proprietors of small and medium-sized enterprises, and any discerning individual keen on establishing a proprietary, self-managed, and highly secure VPN connection atop their chosen trade vps infrastructure.
Essential Preparatory Requirements for OpenVPN Deployment on a VPS
Prior to the commencement of the technical installation procedures, it is absolutely requisite to verify that all necessary preconditions and foundational components are firmly established to guarantee the successful, seamless configuration and subsequent operation of OpenVPN on your Virtual Private Server. A meticulous examination of these prerequisites is provided below:
The Virtual Private Server (VPS) with Secure Shell (SSH) Accessibility
The Virtual Private Server (VPS) constitutes the fundamental host environment—the very backbone—upon which the entire OpenVPN application stack will be installed and executed.
The selection of this foundational server must be executed with deliberate consideration and diligence, focusing on several key parameters:
- Geographic Location: The server’s physical locale must be carefully chosen based on strategic requirements. This consideration is pivotal, particularly when the primary operational objective involves the circumvention of regional geo-restrictions or the optimization of data privacy by selecting a jurisdiction with favorable privacy legislation.
- System Resource Allocation: The provision of adequate computational resources is paramount. It is imperative that the chosen VPS plan allocates sufficient quantities of Central Processing Unit (CPU) power, Random-Access Memory (RAM), and persistent storage capacity. This is especially critical for scenarios anticipating substantial network traffic volumes or a significant concurrent user base, where resource saturation could severely impede performance and reliability.
- Economic and Performance Alignment: The financial commitment (pricing structure) associated with the VPS must be judiciously balanced against the required performance metrics and the unwavering maintenance of a robust security posture. The selected plan must represent an optimal fusion of cost-effectiveness and high-quality service delivery. Furthermore, Secure Shell (SSH) access must be fully provisioned and tested, as it serves as the essential, encrypted administrative conduit for remotely executing the installation and configuration commands on the VPS.
Setting Up the VPS to install OpenVPN
Now that you have your VPS ready, follow these steps to set it up:
- Log in to your VPS: Use SSH to access your VPS with the provided credentials.
ssh username@your-vps-ip
- Update and upgrade packages: Ensure your system is up to date by running the following commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
- Create a non-root user (optional): For added security, create a non-root user and grant them administrative privileges. You can do this by running:
sudo adduser yourusername sudo usermod -aG sudo yourusername
- Configure SSH: To enhance security, modify the SSH configuration to disable root login and password authentication. Edit the SSH configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
- Find and update the following lines:
PermitRootLogin no PasswordAuthentication no
- Restart SSH for changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart sshd
Now, log out and log back in using your new non-root user account.
With your Virtual Private Server (VPS ready and waiting, you’re set to begin an engaging journey into the world of OpenVPN installation. Imagine yourself as an intrepid digital adventurer, navigating the landscapes of online security and privacy. Armed with your trusted VPS and a healthy dose of curiosity, it’s time to delve into this exciting process.
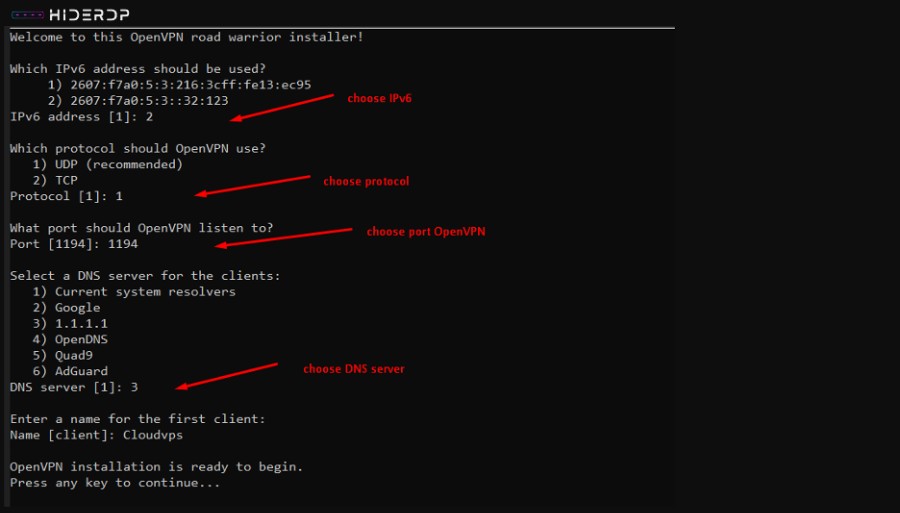
Updating Package Information:
Every great journey begins with preparation, and in the realm of the digital landscape, this means ensuring your VPS has the latest package data. Consider this your equivalent of checking that your maps and tools are ready for the expedition ahead. To get started, run the following command:
sudo apt update
- Installing OpenVPN:
With your preparations complete, it’s time to equip yourself for the core of the adventure—setting up OpenVPN. To install it, execute:
sudo apt install openvpn
- Copy OpenVPN configuration files to the appropriate directory:
sudo cp -r /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/easy-rsa/ /etc/openvpn/
- Navigate to the EasyRSA directory:
cd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa
- Initialize the PKI (Public Key Infrastructure):
sudo ./easyrsa init-pki
- Build the CA (Certificate Authority):
sudo ./easyrsa build-ca
- Generate server and client certificates:
sudo ./easyrsa gen-req server nopass sudo ./easyrsa sign server server sudo ./easyrsa gen-req client nopass sudo ./easyrsa sign client client
Setting Up OpenVPN on a VPS
With OpenVPN installed and the necessary certificates successfully generated, it’s time to proceed with the configuration. Use the steps below to define the essential settings:
Step 1: Set Up the OpenVPN Server Configuration File
Use a text editor to open the server configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/openvpn/server.conf
Please provide the content you’d like added so I can assist with integrating and refining it appropriately:
port 1194 proto udp dev tun ca /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/pki/ca.crt cert /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/pki/issued/server.crt key /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/pki/private/server.key dh none topology subnet server 10.8.0.0 255.255.255.0 push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp" push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.8.8" push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.4.4" cipher AES-256-CBC user nobody group nogroup
This setup allows you to specify key parameters, including the listening port, communication protocol, encryption options, and network topology.
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1Apply the changes:
sudo sysctl -p
Enabling IP forwarding allows your server to efficiently route data between the VPN network and external networks.
Once OpenVPN has been fully configured
the next step is to bring it online and manage its operation:
- Start the OpenVPN Service:
Initiate the OpenVPN service by executing the following command:
sudo systemctl start openvpn@server
This command launches the OpenVPN service, making it operational for your VPN connections.
- Enable Automatic Start at Boot:
To ensure that OpenVPN starts automatically every time your system boots up, run the following command:
sudo systemctl enable openvpn@server
This action guarantees that your VPN service remains consistently available.
- Check the Service Status:
To verify the current status of your OpenVPN service and ensure it’s running as expected, use the following command:
sudo systemctl status openvpn@server
This command provides real-time information about the service’s state, enabling you to confirm that it’s operational and serving your VPN connections.
Conclusion
To conclude, this guide has walked you through a comprehensive, step-by-step process for installing OpenVPN on a Virtual Private Server (VPS).
By adhering to these instructions, you can set up a secure VPN connection to safeguard your online privacy, bypass geo-restrictions, and establish a reliable remote access solution.
While the setup discussed here provides a solid foundation for security, consider exploring advanced configurations and implementing additional protective measures to further strengthen your VPN. Stay secure and make the most of your self-hosted OpenVPN server.

