Floating IPs are a powerful tool for modern web hosting, offering a simple way to manage failover and enhance application uptime. Unlike a static IP address tied to a single server, a floating IP can be instantly moved from one VPS to another. This is particularly useful for achieving high availability and performing maintenance without downtime.
If you’re wondering how to configure a Floating IP on a VPS, this guide will walk you through the essential steps. When you’re ready, you can easily buy Trade VPS solutions to implement these strategies.
Get Started with Floating IPs on Your VPS
The first step in understanding how a floating IP works is to see it as a portable address for your service. Your main VPS has its own private IP, and the floating IP sits on top of it, acting as a public-facing entry point. When a floating IP is assigned to your VPS, all incoming traffic is routed to that server. By learning to Get Started with Floating IPs on Your VPS, you gain the ability to redirect this traffic to a new server in a matter of seconds, should the primary one fail.
To begin, you’ll need a hosting provider that supports floating IPs. Most major cloud providers like DigitalOcean, Vultr, and Linode offer this feature. Once you have a VPS and a floating IP address, the provider’s control panel will be your main tool. You’ll use it to assign the floating IP to your primary VPS. This is the simplest part of learning How to Configure a Floating IP on a VPS.
How to Configure a Floating IP on a VPS
The core of the floating IP setup happens on the server itself. While the control panel handles the assignment, you must configure your VPS to recognize and respond to the floating IP. This involves a few key steps.
First, you need to add the floating IP to your VPS’s network configuration. For Linux servers, this typically means editing a file like /etc/network/interfaces or a similar file for your specific distribution. You’ll add a new line that configures the floating IP as a secondary address for your network interface. This is a crucial step in learning How to Configure a Floating IP on a VPS.
After updating the configuration, you’ll need to apply the changes. This can often be done by restarting the networking service on your server. Once complete, your VPS will be ready to handle traffic directed to the floating IP. It’s important to test this setup to confirm that everything is working as expected.

The Benefits of Floating IPs and How to Configure Them
Now that you know How to Configure a Floating IP on a VPS, let’s look at why it’s so powerful. The main benefit is seamless failover. If your primary VPS goes down for any reason, you can simply unassign the floating IP from the failed server and reassign it to a backup server. This process takes seconds, minimizing downtime and ensuring your services remain online.
This feature is also excellent for planned maintenance. Instead of scheduling maintenance during off-hours, you can spin up a new, updated VPS, move the floating IP to it, and then perform maintenance on the old server without any service interruption. This ability to instantly switch between servers is the key to Get Started with Floating IPs on Your VPS for advanced use cases.
The versatility of floating IPs makes them an indispensable tool. Whether it’s for disaster recovery or routine updates, knowing How to Configure a Floating IP on a VPS provides you with a flexible and reliable solution for managing your online presence.
Troubleshooting and Advanced Use Cases
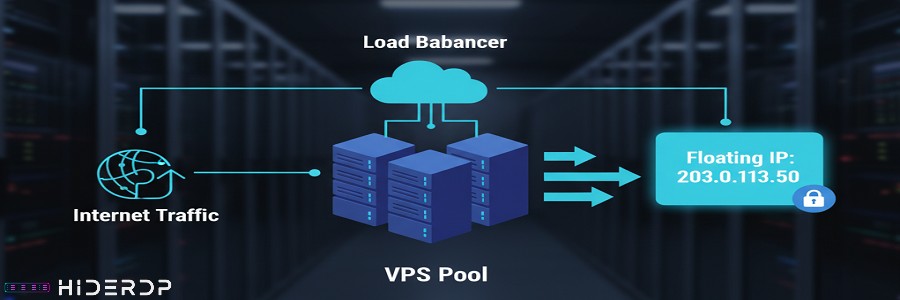
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore more advanced uses for floating IPs. One powerful application is load balancing. By combining a floating IP with a load balancer, you can distribute incoming traffic across multiple VPS instances, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed. This not only improves performance but also provides an extra layer of redundancy.
If you encounter issues, here are a few common troubleshooting tips:
- Floating IP isn’t working after assignment? The first thing to check is your server’s network configuration file. A simple typo can prevent the VPS from recognizing the new IP address. A restart of the networking service or a full server reboot can often resolve this.
- The old IP address is still being used by some visitors? This is a DNS propagation issue. Your floating IP might be active, but some Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and DNS resolvers take time to update their records. You can check a DNS lookup tool to see if the DNS has propagated correctly.
- Failover isn’t instant? The issue might be with your VPS provider’s control panel or API. While the process is usually fast, some providers have a slight delay. Additionally, ensure your backup server is fully configured and ready to handle traffic before initiating a failover.
The versatility of floating IPs makes them an indispensable tool. Whether it’s for disaster recovery, routine updates, or advanced load balancing, knowing How to Configure a Floating IP on a VPS provides you with a flexible and reliable solution for managing your online presence.